

Equivalent fractions are fractions with the same value. For example ½, ⁵⁄₁₀, ⁸⁄₁₆ and ¹⁰⁄₂₀

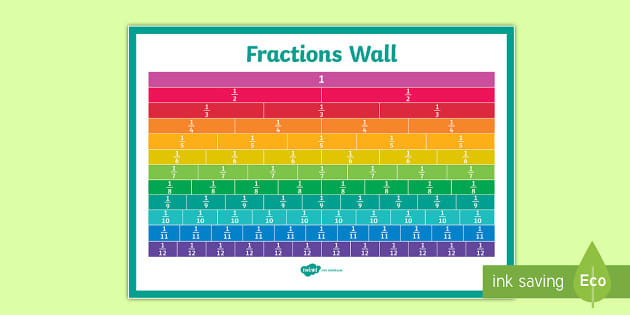
Children often begin to explore equivalent fractions by using visual representations, such as fraction strips, bar models, or a fraction wall. They learn to recognize that fractions with different numerators and denominators can have the same value.
Understanding equivalent fractions enables children to order and compare fractions. Later, they can relate their findings to understanding equivalent fractions, decimals, and percentages.
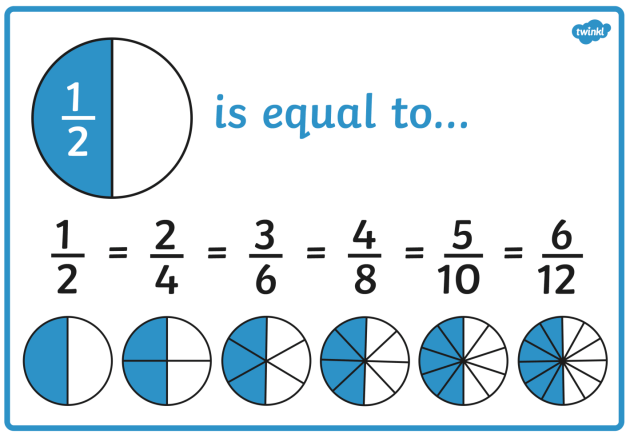
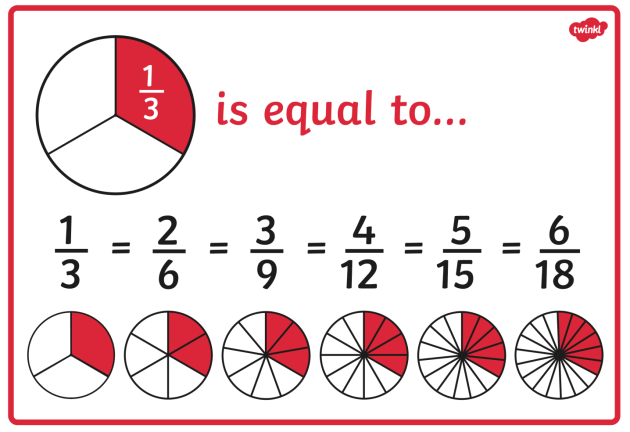
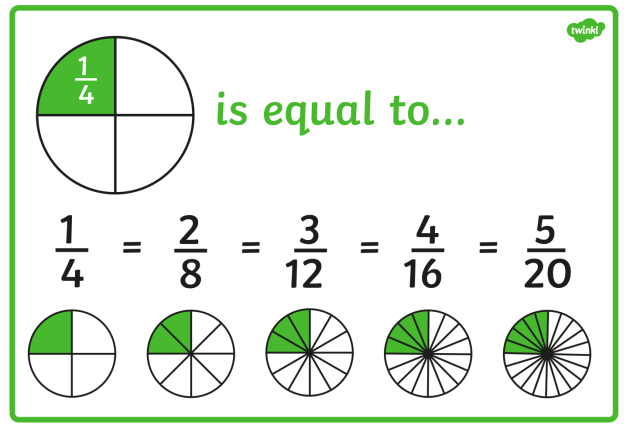
Children can find equivalent fractions by comparing fractions on a bar model or by comparing two number lines.


Later, they will learn to make equivalent fractions by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
They learn to simplify fractions and make the link between common factors and equivalent fractions.
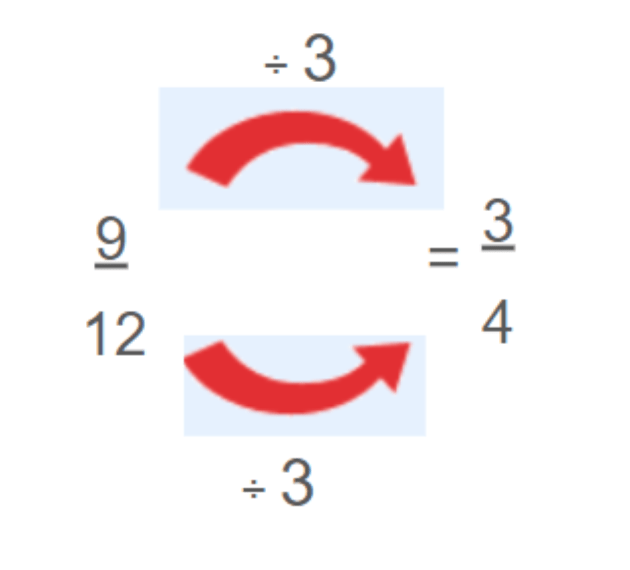
For example, to simplify the fraction 9/12, find a number that both the numerator and denominator can be divided by (also known as a 'common factor'), such as 3.
9/12 and 3/4are equivalent fractions, with 3/4being the fraction in its simplest form.
Children are introduced to fractions in Key Stage 1 and their knowledge and skills are developed each year, throughout the primary education phase. For more information or guidance, please see theNational Curriculum in England: Mathematics Programmes ofStudy.
|
Year 3: Number – Fractions Pupils should be taught to:
Year 4: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals) Pupils should be taught to:
Year 5: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals and Percentages) Pupils should be taught to:
Year 6: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals and Percentages) Pupils should be taught to:
|
|
Key Stage 3 Working mathematically Through the mathematics content, pupils should be taught to: Develop fluency
|
Equivalent fractions are fractions with the same value. For example: 1/2 and 5/10.
Children can begin to explore equivalent fractions using concrete materials (folding and cutting strips of paper, for example) before moving on to visual representations, such as fraction strips, bar models or a fraction wall. They learn to recognise that fractions with different numerators and denominators can have the same value.
Twinkl has plenty of resources to support your teaching on equivalent fractions across the curriculum.

Children often begin to explore equivalent fractions by using visual representations, such as fraction strips, bar models, or a fraction wall. They learn to recognize that fractions with different numerators and denominators can have the same value.
Understanding equivalent fractions enables children to order and compare fractions. Later, they can relate their findings to understanding equivalent fractions, decimals, and percentages.
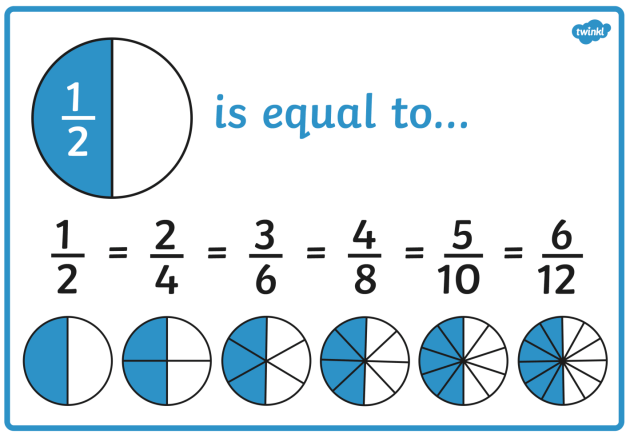
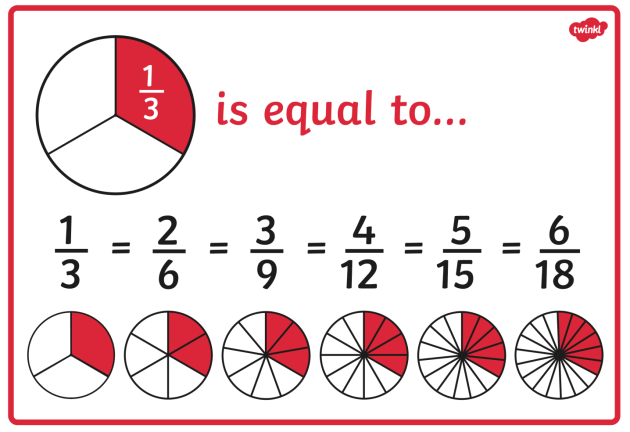
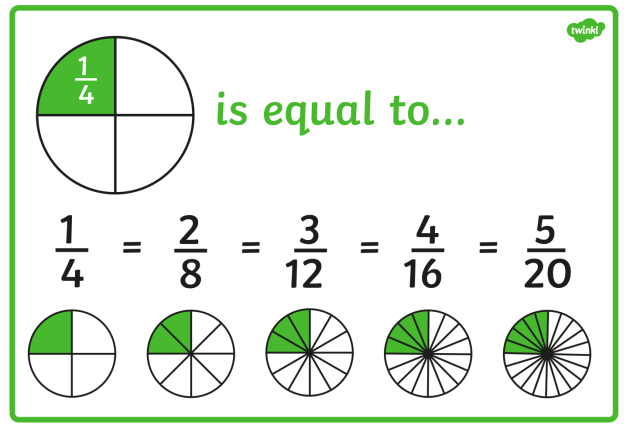
Children can find equivalent fractions by comparing fractions on a bar model or by comparing two number lines.


Later, they will learn to make equivalent fractions by multiplying or dividing both the numerator and the denominator by the same number.
They learn to simplify fractions and make the link between common factors and equivalent fractions.
For example, to simplify the fraction 9/12, find a number that both the numerator and denominator can be divided by (also known as a 'common factor'), such as 3.
9/12 and 3/4are equivalent fractions, with 3/4being the fraction in its simplest form.

Children are introduced to fractions in Key Stage 1 and their knowledge and skills are developed each year, throughout the primary education phase. For more information or guidance, please see theNational Curriculum in England: Mathematics Programmes ofStudy.
|
Year 3: Number – Fractions Pupils should be taught to:
Year 4: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals) Pupils should be taught to:
Year 5: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals and Percentages) Pupils should be taught to:
Year 6: Number – Fractions (Including Decimals and Percentages) Pupils should be taught to:
|
|
Key Stage 3 Working mathematically Through the mathematics content, pupils should be taught to: Develop fluency
|
Equivalent fractions are fractions with the same value. For example: 1/2 and 5/10.
Children can begin to explore equivalent fractions using concrete materials (folding and cutting strips of paper, for example) before moving on to visual representations, such as fraction strips, bar models or a fraction wall. They learn to recognise that fractions with different numerators and denominators can have the same value.
Twinkl has plenty of resources to support your teaching on equivalent fractions across the curriculum.