Transistor Technologies How to use a MOSFET as a switch?
Related Vendors
MOSFET is one of the best transistors to perform switching functions in a circuit. The voltage-controlled transistor is thermally stable and provides fast switching. MOSFET behaves like a switch in cut-off and saturation regions of operation. Here is an article to understand the operation of MOSFET as a switch and its advantages.

When is it useful to use MOSFET as a switch?
Can we use a Depletion mode MOSFET?
Depletion Mode MOSFET: Depletion mode MOSFET is a “normally ON” device. The transfer characteristics of Depletion type MOSFET is a graph of drain current ID on Y-axis against gate-to-source VGS on the X-axis.
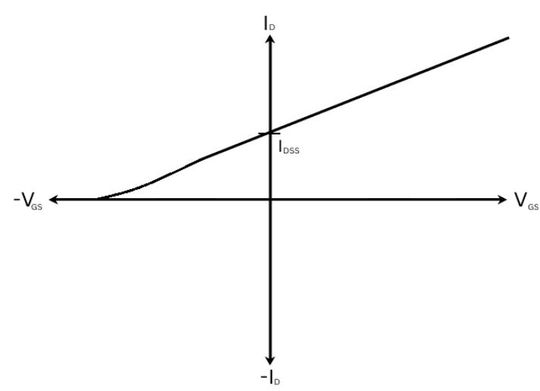
MOSFET operates when gate-to-source voltage VGS is negative and positive both. Such a device cannot be used for switching purposes because it is “normally ON”.
Can we use Enhancement mode MOSFET?
Enhancement Mode MOSFET: Enhancement Mode MOSFET is a great choice for switching purposes because it is a “normally OFF” device that can be turned on. The transfer characteristics of Enhancement mode MOSFET is a graph of drain current ID on the Y-axis against gate-to-source VGS on the X-axis. VT is the threshold voltage beyond which the device turns on.
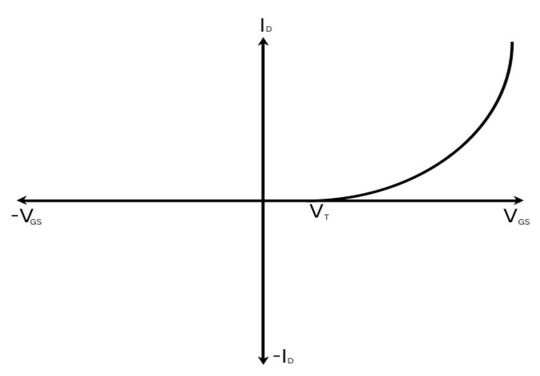
How does a MOSFET work as a switch?
The transistor MOSFET works as a switch in two operating modes- cut-off and saturation region. MOSFET acts as a short circuit or closed switch in the saturation region and an open switch in the cut-off region.
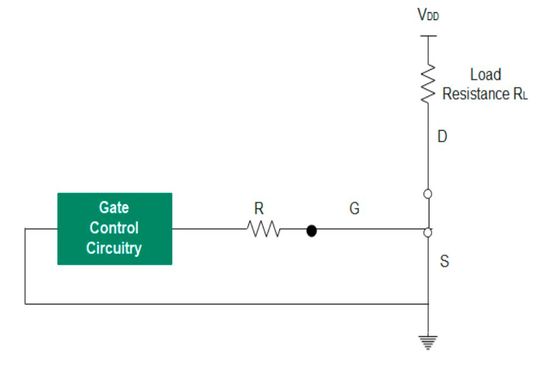
A MOSFET switching diagram includes load resistance, and gate control circuitry that can be a microcontroller.
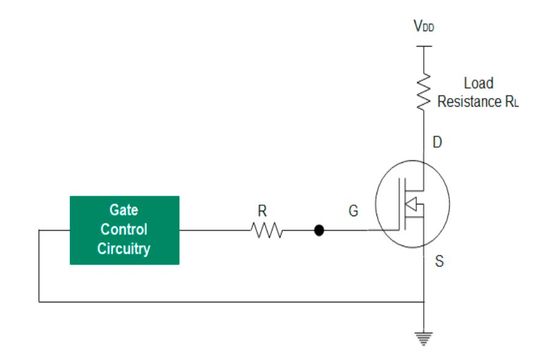
Enhancement mode N-channel MOSFET operating modes for switching:
| Condition | Operation |
| VGS < VThreshold | Open switch (OFF) |
| VGS > VThreshold | Short circuit (ON) |
MOSFET as an open switch (VGS < VT)
When VGS is less than VT but not equal to zero, MOSFET is in the cut-off region. Since VGS < VThreshold, no channel formation takes place, and no current flows through the MOSFET.
The transistor behaves like an open circuit and is logically “OFF”.
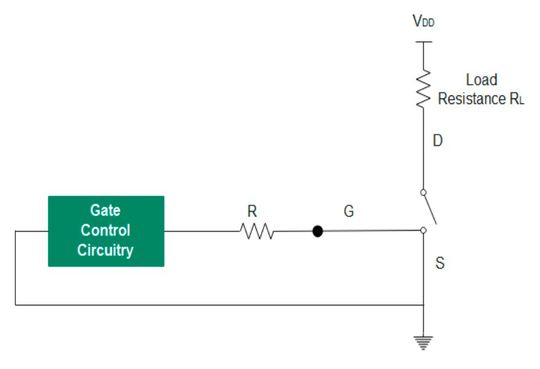
MOSFET as a short circuit (VGS > VT)
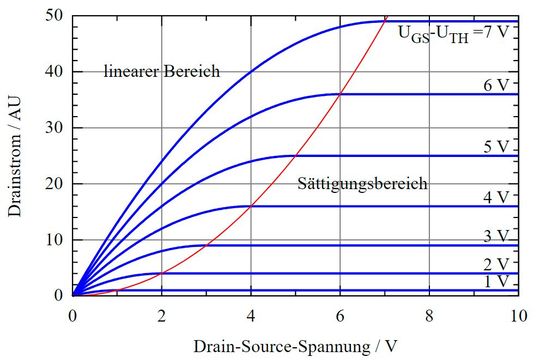
Drain characteristics of an enhancement mode MOSFET are obtained by plotting a graph between drain current ID on the Y-axis and drain-to-source voltage VDS on the X-axis for different values of VGS.
For a voltage VGS > VT, voltage VDS is increased. The drain current ID increases linearly with increasing VDS until the saturation point-ohmic region. Beyond the saturation point, the drain current ID remains constant and does not change with increasing VDS .
The region of operation is termed as the saturation region where MOSFET acts like a short circuit or closed switch and is logically “ON”.
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/dc/a7/dca77894a4c67d65ad70173fd4a6475c/0111258009.jpeg)
TRANSISTOR TECHNOLOGY
How to use a transistor as a switch?
What are the advantages of using MOSFET as a switch?
There are many advantages of using a MOSFET transistor as a switch.
- There is less noise in semiconductor switches compared to mechanical switches.
- MOSFETs are more thermally stable than BJT because of the positive temperature coefficient.
- Power MOSFETs offer nanosecond switching.
- Low maintenance because there are no moving parts.
- MOSFETs are smaller in size and weight.
- MOSFET switches have lower switching losses.
References
- https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/transistor/tran_7.html
- https://youtu.be/UJkHL-6mn8s
(ID:49659242)




:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f1/de/f1de0c5e59f67aa7f2572932ec1f4be9/0118079617.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/87/7b/877b3ce1be09eb309e4e952ddeed5f76/0118162459.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/53/fb/53fb719e1b7ca51e26a600beb4973caa/0117927695.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/20/5f/205f55e131397019d7d0b4c93afd7692/0117866888.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/c1/f2/c1f297688969aa72399076f01dda34bb/0118112747.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/13/e3/13e3bfa7ebef959901dc5cbf86be46e5/0118079609.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/9b/f4/9bf4c897c21cec0c927124f0b716f48d/0117966730.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/da/ff/daff35bdf441484576a996352b0b8b5e/0117868043.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/08/4b/084bdffffea262d1988a4a9092ac74a6/0118170678.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/df/6d/df6d4da46e35064efa91d9b8658131a0/0118004183.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/3e/9e/3e9ed788776623d655ec51f92e151ef4/0117774205.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/35/f2/35f243dd4bd4d57587bd7e4f7a85d6fa/0117752002.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/a0/22/a0220573ab4987d56f248dd3d9712760/0117238956.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/4e/13/4e1363ce48fc85e61d98a235969d4638/0116922802.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/70/14/7014ecedef4954eb2b455e5a522804b7/0102877609.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/8d/a5/8da5b7876ca5418c7a6666a4b6fe01ed/0116529715.jpeg)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/63/c7/63c7da97be945/diotec.png)
:fill(fff,0)/p7i.vogel.de/companies/62/95/6295c25c8dc1a/schunk-sonosystems-300dpi.png)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/34/24/34243ab470fd7bcd3cfd4a7564c2b4eb/0111077180.jpeg)
:quality(80)/p7i.vogel.de/wcms/f8/20/f8200c20833f88f20ef5ba0f85550259/0110796538.jpeg)